By Christopher Bing
WASHINGTON (Reuters) – The U.S. government plans to launch a program in roughly one month that narrowly focuses on protecting voter registration databases and systems ahead of the 2020 presidential election.
These systems, which are widely used to validate the eligibility of voters before they cast ballots, were compromised in 2016 by Russian hackers seeking to collect information. Intelligence officials are concerned that foreign hackers in 2020 not only will target the databases but attempt to manipulate, disrupt or destroy the data, according to current and former U.S. officials.
“We assess these systems as high risk,” said a senior U.S. official, because they are one of the few pieces of election technology regularly connected to the Internet.
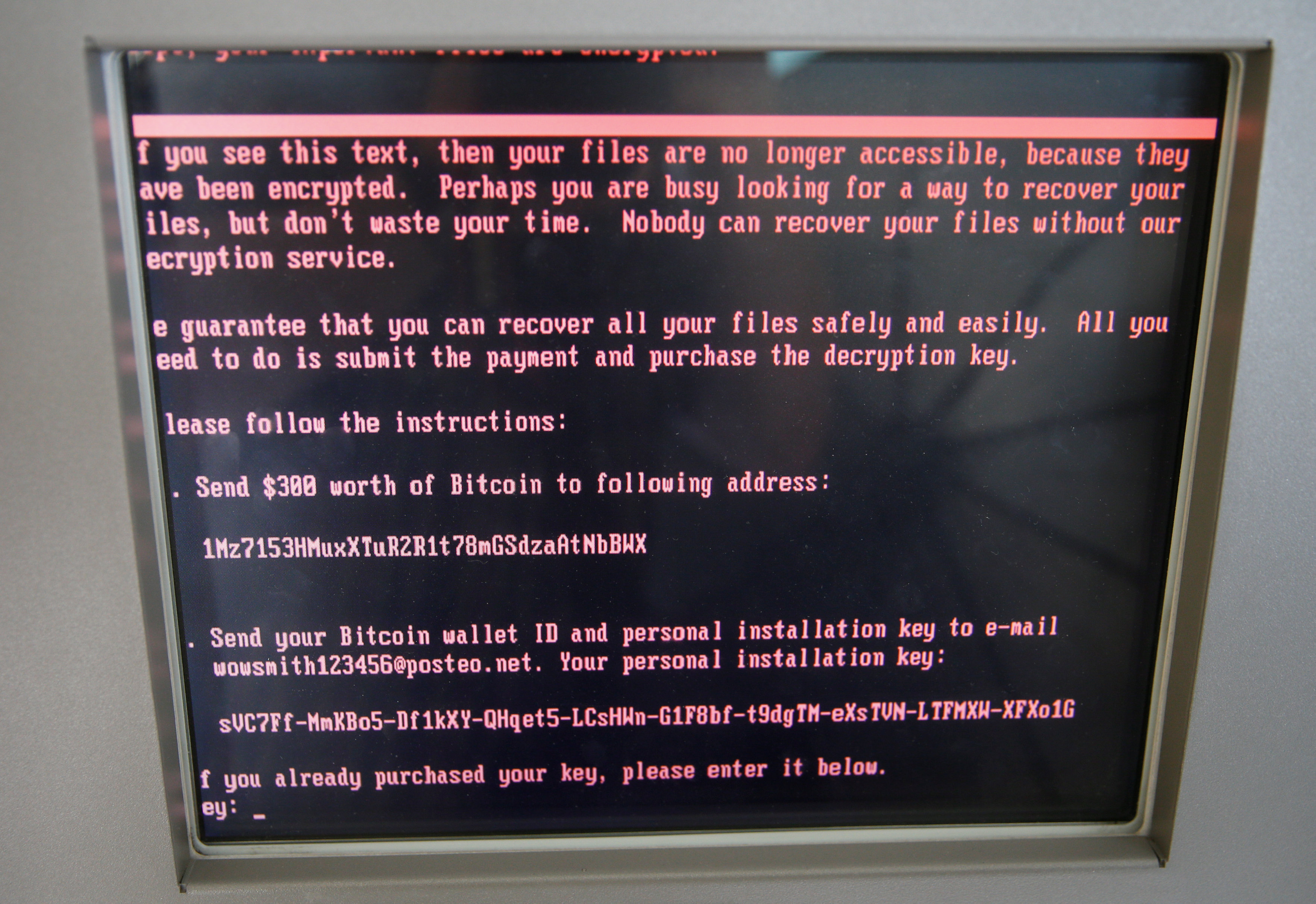
The Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency, or CISA, a division of the Homeland Security Department, fears the databases could be targeted by ransomware, a type of virus that has crippled city computer networks across the United States, including recently in Texas, Baltimore and Atlanta.
“Recent history has shown that state and county governments and those who support them are targets for ransomware attacks,” said Christopher Krebs, CISA’s director. “That is why we are working alongside election officials and their private sector partners to help protect their databases and respond to possible ransomware attacks.”
A ransomware attack typically locks an infected computer system until payment, usually in the form of cryptocurrency, is sent to the hacker.
The effort to counter ransomware-style cyberattacks aimed at the election runs parallel to a larger intelligence community directive to determine the most likely vectors of digital attack in the November 2020 election, according to current and former U.S. officials.
“It is imperative that states and municipalities limit the availability of information about electoral systems or administrative processes and secure their websites and databases that could be exploited,” the FBI said in a statement, supporting the Homeland Security initiative.
CISA’s program will reach out to state election officials to prepare for such a ransomware scenario. It will provide educational material, remote computer penetration testing, and vulnerability scans as well as a list of recommendations on how to prevent and recover from ransomware.
These guidelines, however, will not offer advice on whether a state should ultimately pay or refuse to pay ransom to a hacker if one of its systems is already infected.
“Our thought is we don’t want the states to have to be in that situation,” said a Homeland Security official. “We’re focused on preventing it from happening.”
Over the last two years, cybercriminals and nation state hacking groups have used ransomware to extort victims and create chaos. In one incident in 2017, which has since been attributed to Russian hackers, a ransomware virus was used to mask a data deletion technique, rendering victim computers totally unusable.
That attack, dubbed “NotPetya,” went on to damage global corporations, including FedEx and Maersk, which had offices in Ukraine where the malware first spread.
The threat is concerning because of its potential impact on voting results, experts say.
“A pre-election undetected attack could tamper with voter lists, creating huge confusion and delays, disenfranchisement, and at large enough scale could compromise the validity of the election,” said John Sebes, chief technology officer of the OSET Institute, an election technology policy think tank.
The databases are also “particularly susceptible to this kind of attack because local jurisdictions and states actively add, remove, and change the data year-round,” said Maurice Turner, a senior technologist with the Center for Democracy and Technology. “If the malicious actor doesn’t provide the key, the data is lost forever unless the victim has a recent backup.”
Nationwide, the local governments that store and update voter registration data are typically ill-equipped to defend themselves against elite hackers.
State election officials told Reuters they have improved their cyber defenses since 2016, including in some cases preparing backups for voter registration databases in case of an attack. But there is no common standard for how often local governments should create backups, said a senior Homeland Security official.
“We have to remember that this threat to our democracy will not go away, and concern about ransomware attacks on voter registration databases is one clear example,” said Vermont Secretary of State Jim Condos. “We’re sure the threat is far from over.”
(Reporting by Christopher Bing; Editing by Steve Orlofsky)