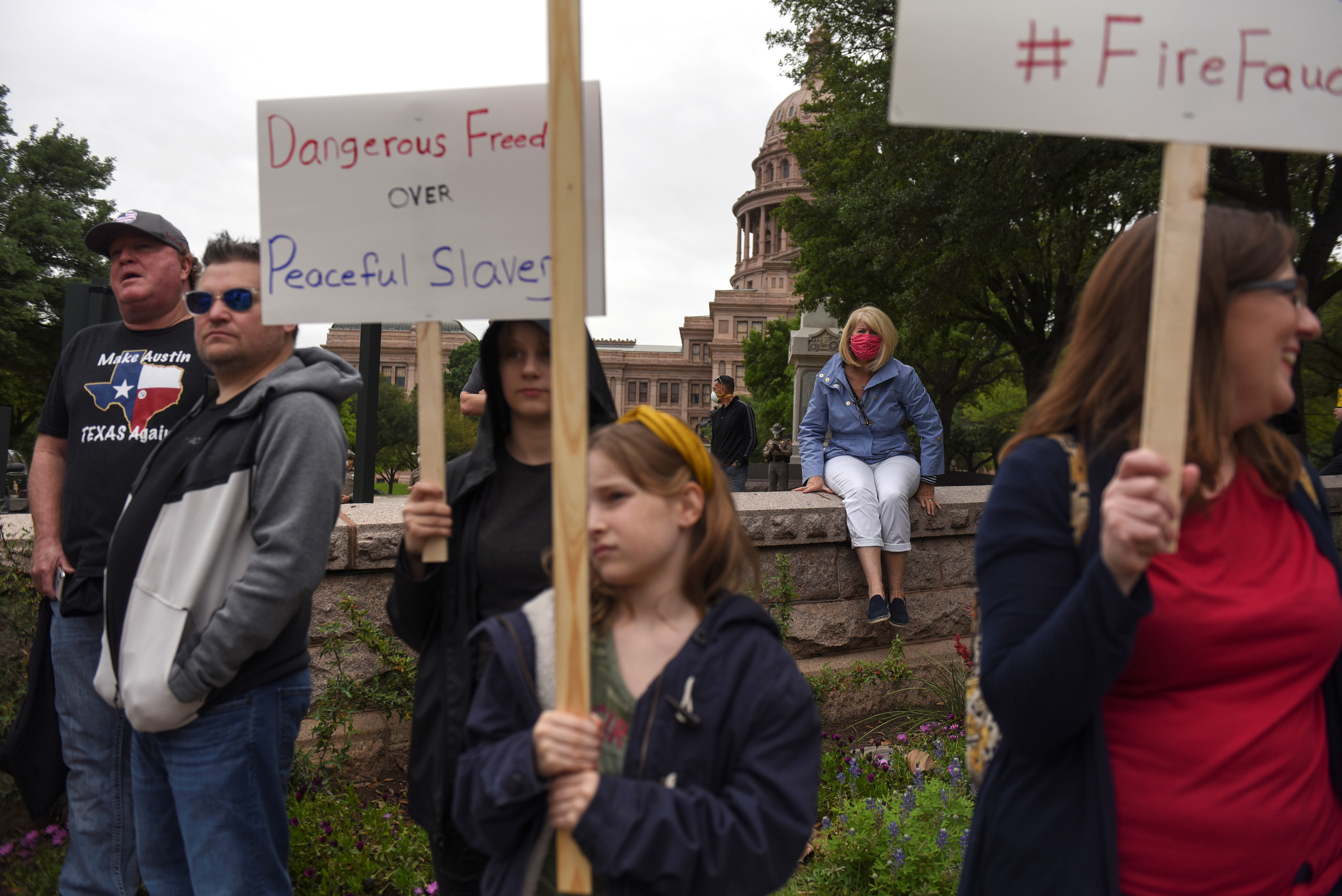
By Maria Caspani and Nathan Layne
NEW YORK (Reuters) – Demonstrations to demand an end to stay-at-home measures that have pummelled the U.S. economy spread to Texas on Saturday as the governor at the epicentre of the U.S. coronavirus crisis said his state of New York may finally be past the worst.
New York, which has recorded nearly half the country’s deaths from COVID-19, the respiratory disease caused by the highly infectious virus, on Saturday reported 540 coronavirus-related deaths for April 17, down from 630 a day earlier and the lowest daily tally since April 1.
The number of patients in the state requiring intensive care and ventilators to help them breathe was also down.
“If you look at the past three days, you could argue that we are past the plateau and we’re starting to descend, which would be very good news,” New York Governor Andrew Cuomo said in his daily briefing.
Some 2,000 people were still being hospitalized with COVID-19 every day, Cuomo said, and he noted 36 of the latest New York deaths occurred at nursing homes, which have been ravaged by the pandemic nationwide.
In neighboring New Jersey, both the number of new hospitalizations and new coronavirus cases were also slightly down from the day before, Governor Phil Murphy said. But he added: “We are not out of the woods, we have not yet plateaued.”
Illinois reported 125 new coronavirus deaths and an additional 1,585 cases but said the growth rate was slowing.
Murphy said he had a “concerning” call with Senate minority leader and fellow Democrat Chuck Schumer, who told him there was no momentum in the U.S. Congress for direct aid to states whose economies were suffering from the stay-at-home orders aimed at curbing the spread of the virus.
Without federal aid, the state will see “historic” layoffs, he said.
More than 22 million Americans have filed for unemployment benefits in the past month as closures of businesses and schools and severe travel restrictions have hammered the economy.
But an influential research model said late on Friday the strict adherence to the orders imposed in 42 of the 50 U.S. states was a key factor behind an improved outlook for the country’s coronavirus death toll.
The University of Washington’s predictive model, regularly updated and often cited by state public health authorities and White House officials, projected the virus would take 60,308 U.S. lives by Aug. 4, down 12% from a forecast earlier in the week.
The model predicted some states may be able to begin safely easing restrictions as early as May 4.
PUSHBACK
Many have already started pushing back against the measures.
Governor Murphy chastised an official in Atlantic County, home to Atlantic City, for expressing frustration in a Facebook post over the effect of the closures on the casino-dependent local economy. County surrogate Jim Curcio said his comments were his personal opinion.
“I’ve lived here all my life and when we go into a recession here we seem to be the last to come out of it and people suffer terribly and the most vulnerable suffer the most,” Curcio told Reuters on Saturday. “What is happening to the private sector is my breaking my heart.”
On Saturday, several dozen protesters gathered in the Texas capital of Austin chanting “USA! USA!” and “Let us work!”
In Brookfield, Wisconsin, hundreds of demonstrators cheered as they lined a main road and waved American flags to protest at the extension of that state’s “safer at home” order.
Earlier in the week, scattered protests erupted in the capitols of Ohio, Minnesota, Michigan and Virginia. The demonstrators mostly flouted the social-distancing rules and did not wear the face masks recommended by public health officials.
As of Friday night, New York has mandated the statewide wearing of masks for anyone out in public and unable to practice social distancing.
Republican President Donald Trump appeared to encourage protesters with a series of Twitter posts on Friday calling for them to “LIBERATE” Michigan, Minnesota and Virginia, all run by Democratic governors.
Trump had touted a thriving economy as the best case for his re-election in November.
Several states, including Ohio, Michigan, Texas and Florida, have said they aim to reopen parts of their economies, perhaps by May 1 or even sooner, but appeared to be staying cautious.
Florida’s Republican governor Ron DeSantis reopened some beaches with restrictions from Friday evening, but also said on Saturday that schools will remain closed and continue distance learning the rest of this school year.
Fellow Republican Governor Greg Abbott of Texas has also extended school closures to the end of the academic year.
Health experts say that to avoid a second wave of infections as people return to work, extensive testing must be available to track infections, as well as contact tracing and antibody testing to learn who had been previously infected and might have some immunity.
Vice President Mike Pence said on Friday the United States had the capacity to do a sufficient amount of testing for states to move into a phase one of reopening.
Governors and state health officials say there is nowhere near enough test kits and equipment available, however.
The United States has by far the world’s largest number of confirmed coronavirus cases, with more than 720,000 infections and over 37,000 deaths.
The handful of states that did not issue stay-at-home orders have all seen significant surges in new cases.
(Reporting by Nathan Layne in Wilton, Connecticut, Maria Caspani in New York, Jennifer Hiller in Houston and Idrees Ali in Washington; Writing by Bill Berkrot and Sonya Hepinstall; Editing by Daniel Wallis)












